Can we use Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) for image classification?
Yes, ANNs can be used for image classification. However, a drawback is the substantial computational requirements, often necessitating the computation of approximately 500 million weights.
Disadvantages of using ANN for image classification:
- Excessive computation
- Treats local pixels the same as distant pixels
- Sensitivity to the location of an object in the image
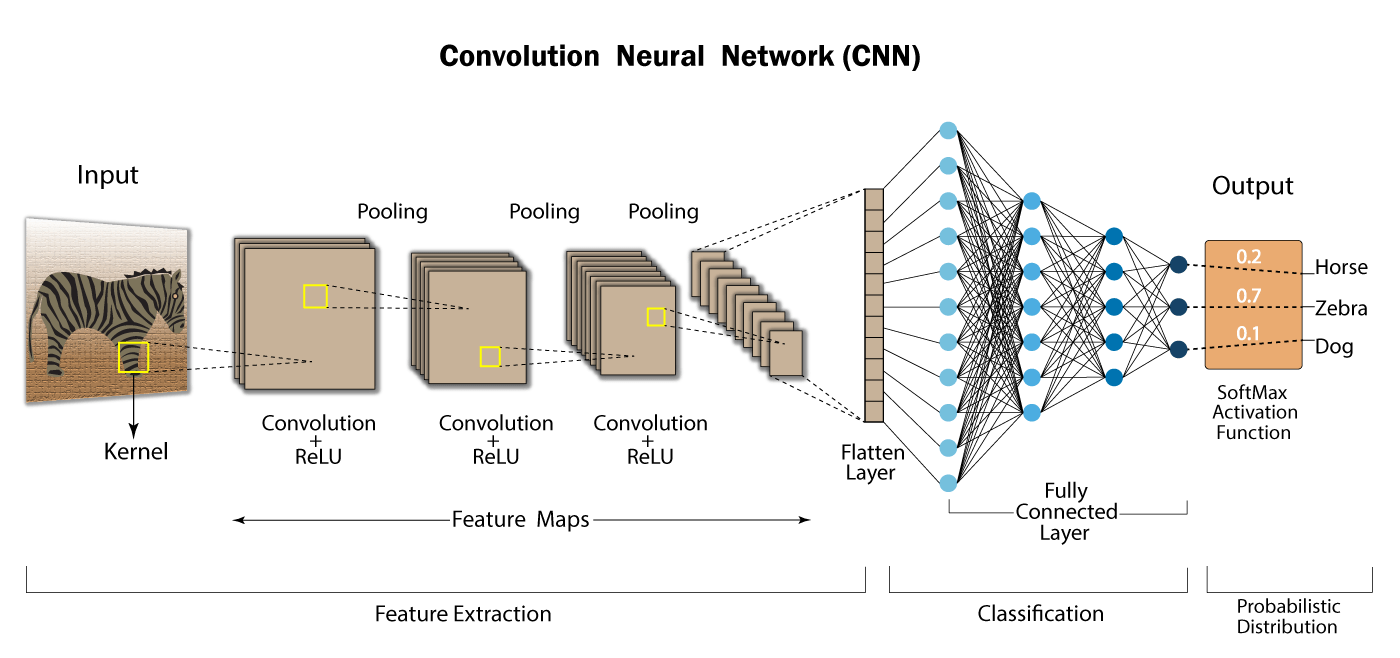
Recognition in image classification relies on identifying features. Computers understand these features through filters, where each element is multiplied with the original image to create a feature map through convolution operations.
Convolution:
- Connection sparsity reduces overfitting.
- Convolution combined with pooling provides location-invariant feature detection.
- Promotes parameter sharing.
Filters in convolution are essentially feature detectors, and using ‘n’ filters results in ‘n’ feature maps.
Neural networks introduce variety to input and classify in a generic way. The use of Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) helps the model achieve non-linearity. To address computational challenges, pooling layers are employed, aiding in size reduction and position-invariant feature detection.
Pooling:
Various pooling methods like max pooling and average pooling exist.
- Diminishes dimensions and computation
- Mitigates overfitting by reducing parameters
- Enhances model tolerance to variant distortions
In Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), rotated and scaled data are essential. Therefore, data augmentation methods from existing training samples are employed.
In this notebook, I trained both an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) and a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for image classification. The goal is to showcase the differences in performance between the two approaches.